平衡机器人,使用带有 BluBug 和 Android 的车轮和 imu 6 轴传感器平衡机器人。
自平衡倒立摆机器人。构建很简单,软件是免费和开源的,基于 Arduino。
自平衡机器人的核心是 IMU,由 3 轴速率陀螺仪、加速度计组成。这 6 个传感器每秒最多采样 1,000 次,并与一段称为 DCM(方向余弦矩阵算法)的代码集成在一起,这是一种结合了每个传感器最佳属性的数学滤波器。机器人的高级代码可以根据平衡的需要简单地询问 DCM 机器人的角度和旋转速率。
代码区
#include <PID_v1.h>
#include <LMotorController.h>
#include “I2Cdev.h”
#include “MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h”
#if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE
#include “Wire.h”
#endif
#define LOG_INPUT 0
#define MANUAL_TUNING 0
#define LOG_PID_CONSTANTS 0 //MANUAL_TUNING must be 1
#define MOVE_BACK_FORTH 0
#define MIN_ABS_SPEED 30
//MPU
MPU6050 mpu;
#define OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL
// MPU control/status vars
#define INTERRUPT_PIN 2 // use pin 2 on Arduino Uno & most boards
#define LED_PIN 13 // (Arduino is 13, Teensy is 11, Teensy++ is 6)
bool blinkState = false;
// MPU control/status vars
bool dmpReady = false; // set true if DMP init was successful
uint8_t mpuIntStatus; // holds actual interrupt status byte from MPU
uint8_t devStatus; // return status after each device operation (0 = success, !0 = error)
uint16_t packetSize; // expected DMP packet size (default is 42 bytes)
uint16_t fifoCount; // count of all bytes currently in FIFO
uint8_t fifoBuffer[64]; // FIFO storage buffer
// orientation/motion vars
Quaternion q; // [w, x, y, z] quaternion container
VectorInt16 aa; // [x, y, z] accel sensor measurements
VectorInt16 aaReal; // [x, y, z] gravity-free accel sensor measurements
VectorInt16 aaWorld; // [x, y, z] world-frame accel sensor measurements
VectorFloat gravity; // [x, y, z] gravity vector
float euler[3]; // [psi, theta, phi] Euler angle container
float ypr[3]; // [yaw, pitch, roll] yaw/pitch/roll container and gravity vector
// packet structure for InvenSense teapot demo
uint8_t teapotPacket[14] = { ‘$’, 0x02, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0x00, 0x00, ‘\r’, ‘\n’ };
//PID
#if MANUAL_TUNING
double kp , ki, kd;
double prevKp, prevKi, prevKd;
#endif
double originalSetpoint = 174.29;
double setpoint = originalSetpoint;
double movingAngleOffset = 0.3;
double input, output;
int moveState=0; //0 = balance; 1 = back; 2 = forth
#if MANUAL_TUNING
PID pid(&input, &output, &setpoint, 0, 0, 0, DIRECT);
#else
PID pid(&input, &output, &setpoint, 70, 240, 1.9, DIRECT);
#endif
//MOTOR CONTROLLER
int ENA = 3;
int IN1 = 4;
int IN2 = 8;
int IN3 = 5;
int IN4 = 7;
int ENB = 6;
LMotorController motorController(ENA, IN1, IN2, ENB, IN3, IN4, 0.6, 1);
//timers
long time1Hz = 0;
long time5Hz = 0;
// ================================================================
// === INTERRUPT DETECTION ROUTINE ===
// ================================================================
volatile bool mpuInterrupt = false; // indicates whether MPU interrupt pin has gone high
void dmpDataReady() {
mpuInterrupt = true;
}
void setup()
{
// join I2C bus (I2Cdev library doesn’t do this automatically)
#if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE
Wire.begin();
Wire.setClock(400000); // 400kHz I2C clock. Comment this line if having compilation difficulties
#elif I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_BUILTIN_FASTWIRE
Fastwire::setup(400, true);
#endif
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial); // wait for Leonardo enumeration, others continue immediately
// initialize device
Serial.println(F(“Initializing I2C devices…”));
mpu.initialize();
pinMode(INTERRUPT_PIN, INPUT);
// verify connection
Serial.println(F(“Testing device connections…”));
Serial.println(mpu.testConnection() ? F(“MPU6050 connection successful”) : F(“MPU6050 connection failed”));
// wait for ready
Serial.println(F(“\nSend any character to begin DMP programming and demo: “));
while (Serial.available() && Serial.read()); // empty buffer
while (!Serial.available()); // wait for data
while (Serial.available() && Serial.read()); // empty buffer again
// load and configure the DMP
Serial.println(F(“Initializing DMP…”));
devStatus = mpu.dmpInitialize();
// supply your own gyro offsets here, scaled for min sensitivity
mpu.setXGyroOffset(220);
mpu.setYGyroOffset(76);
mpu.setZGyroOffset(-85);
mpu.setZAccelOffset(1788); // 1688 factory default for my test chip
// make sure it worked (returns 0 if so)
if (devStatus == 0)
{
// turn on the DMP, now that it’s ready
Serial.println(F(“Enabling DMP…”));
mpu.setDMPEnabled(true);
// enable Arduino interrupt detection
Serial.println(F(“Enabling interrupt detection (Arduino external interrupt 0)…”));
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN), dmpDataReady, RISING);
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
// set our DMP Ready flag so the main loop() function knows it’s okay to use it
Serial.println(F(“DMP ready! Waiting for first interrupt…”));
dmpReady = true;
// get expected DMP packet size for later comparison
packetSize = mpu.dmpGetFIFOPacketSize();
//setup PID
pid.SetMode(AUTOMATIC);
pid.SetSampleTime(10);
pid.SetOutputLimits(-255, 255);
}
else
{
// ERROR!
// 1 = initial memory load failed
// 2 = DMP configuration updates failed
// (if it’s going to break, usually the code will be 1)
Serial.print(F(“DMP Initialization failed (code “));
Serial.print(devStatus);
Serial.println(F(“)”));
}
// configure LED for output
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
// if programming failed, don’t try to do anything
if (!dmpReady) return;
// wait for MPU interrupt or extra packet(s) available
while (!mpuInterrupt && fifoCount < packetSize)
{
//no mpu data – performing PID calculations and output to motors
pid.Compute();
motorController.move(output, MIN_ABS_SPEED);
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
if (currentMillis – time1Hz >= 1000)
{
loopAt1Hz();
time1Hz = currentMillis;
}
if (currentMillis – time5Hz >= 5000)
{
loopAt5Hz();
time5Hz = currentMillis;
}
}
// reset interrupt flag and get INT_STATUS byte
mpuInterrupt = false;
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
// get current FIFO count
fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
// check for overflow (this should never happen unless our code is too inefficient)
if ((mpuIntStatus & 0x10) || fifoCount == 1024)
{
// reset so we can continue cleanly
mpu.resetFIFO();
Serial.println(F(“FIFO overflow!”));
// otherwise, check for DMP data ready interrupt (this should happen frequently)
}
else if (mpuIntStatus & 0x02)
{
// wait for correct available data length, should be a VERY short wait
while (fifoCount < packetSize) fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
// read a packet from FIFO
mpu.getFIFOBytes(fifoBuffer, packetSize);
// track FIFO count here in case there is > 1 packet available
// (this lets us immediately read more without waiting for an interrupt)
fifoCount -= packetSize;
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetYawPitchRoll(ypr, &q, &gravity);
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL
// display Euler angles in degrees
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetYawPitchRoll(ypr, &q, &gravity);
Serial.print(“ypr\t”);
Serial.print(ypr[0] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print(“\t”);
Serial.print(ypr[1] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print(“\t”);
Serial.println(ypr[2] * 180/M_PI);
#endif
input = ypr[1] * 180/M_PI + 180;
}
}
void loopAt1Hz()
{
#if MANUAL_TUNING
setPIDTuningValues();
#endif
}
void loopAt5Hz()
{
#if MOVE_BACK_FORTH
moveBackForth();
#endif
}
//move back and forth
void moveBackForth()
{
moveState++;
if (moveState > 2) moveState = 0;
if (moveState == 0)
setpoint = originalSetpoint;
else if (moveState == 1)
setpoint = originalSetpoint – movingAngleOffset;
else
setpoint = originalSetpoint + movingAngleOffset;
}
//PID Tuning (3 potentiometers)
#if MANUAL_TUNING
void setPIDTuningValues()
{
readPIDTuningValues();
if (kp != prevKp || ki != prevKi || kd != prevKd)
{
#if LOG_PID_CONSTANTS
Serial.print(kp);Serial.print(“, “);Serial.print(ki);Serial.print(“, “);Serial.println(kd);
#endif
pid.SetTunings(kp, ki, kd);
prevKp = kp; prevKi = ki; prevKd = kd;
}
}
void readPIDTuningValues()
{
int potKp = analogRead(A0);
int potKi = analogRead(A1);
int potKd = analogRead(A2);
kp = map(potKp, 0, 1023, 0, 25000) / 100.0; //0 – 250
ki = map(potKi, 0, 1023, 0, 100000) / 100.0; //0 – 1000
kd = map(potKd, 0, 1023, 0, 500) / 100.0; //0 – 5
}
#endif
在下面直接下载
基于Arduino UNO的自平衡机器人
22i2复制
没有复制

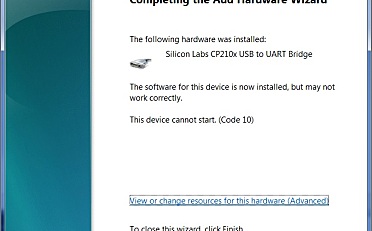
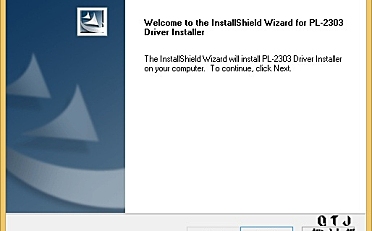
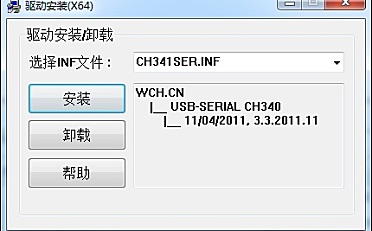




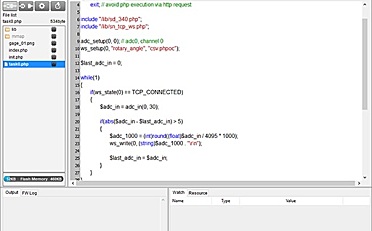















姿态解算是用DMP么
过期了~大佬